前言
对于 java 日志框架体系相信大家都不陌生,哪怕是初入职场的年轻人也能脱口而出 slf4j + logback 或者 slf4j + log4j2 这样的日志组合,slf4j 作为日志门面不提供具体的日志实现,具体实现委托给具体的日志框架完成,接口和实现分离,日志实现的切换对上层调用方透明。方案看似很完美,但现实很骨感:由于历史原因,一些三方框架可能会使用特定的日志实现,比如 curator 就直接使用的 log4j;还有一些框架会使用另一款日志门面 common-logging,比如 spring。为了统一项目里的所有日志实现,slf4j 也提供了它的解决方案 —— “日志桥接器”,通过编译期静态绑定的方式将其他框架的日志 API 调用转发到 slf4j 上来,最终实现大一统。
结局很完美,但过程可能会比较艰辛,在实践过程中我们需要逐一分析项目的日志依赖包,引入正确的日志绑定器、桥接器,排除特定的日志包,由于日志框架的纷繁复杂,在新建项目或者自己引入三方框架的过程中,很容易出现日志配置错误的问题,比如自己之前就遇到过由于配置不当导致 spring 日志无法输出的情况,虽然 spring-boot-starter-logging 的出现部分缓解了这个问题,但在最近一次开发中,还是遇到了 spring-boot 项目引入 dubbo 后无法打印 dubbo 日志的问题。
就算之前成功配置过一次,理清了各个日志包之间的关系,但过一段时间之后也很可能因为记忆模糊,再次被各种日志包名绕进去,比如记不清 “slf4j-log4j12” 和 “log4j-over-slf4j” 哪个是绑定器哪个是桥接器,”log4j-over-slf4j” 和 “log4j-to-slf4j” 又是什么区别,这里面太多弯弯绕。
这篇文章的初衷就是一次捋清上述问题,作为日志框架配置的备忘录。
slf4j 日志过程
本文的目的是梳理 slf4j 日志实践的全过程,为日志配置实践提供参考,所以不会涉及对日志框架原理的详细描述。
下面以这个具体case为例,简单回顾下 slf4j 日志打印的全过程:
- 使用特定的 slf4j 桥接器,将 common-logging 日志调用转成 slf4j 的调用
- 使用绑定器,将 slf4j 的日志调用委托给 log4j,由 log4j 框架实现实际的日志输出
1 | Component |
下面开始罗列 slf4j 具体的绑定器和桥接器,以及他们之间的区别。(图片来自 官网)
slf4j 绑定器:接口绑定多种实现
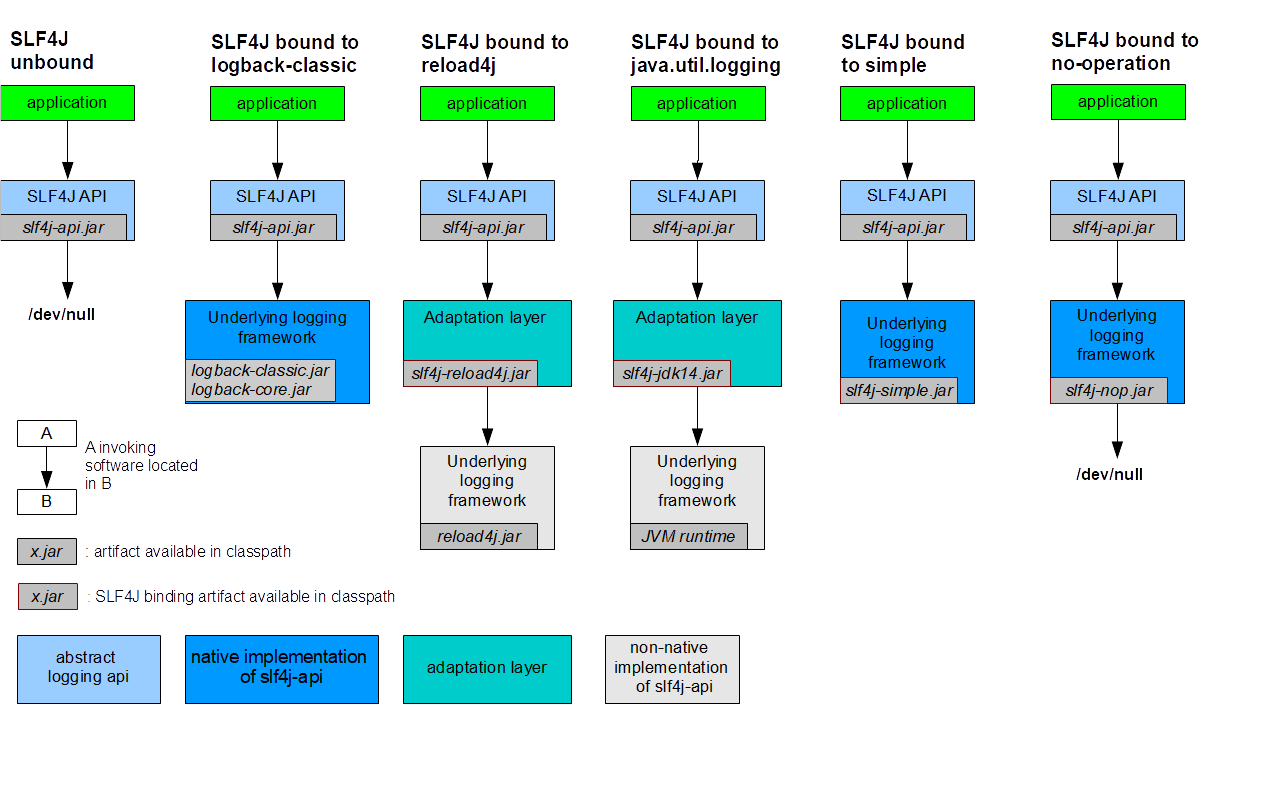
common-logging & slf4j 同属于日志接口,具体实现委派给具体的日志实现包,和 common logging 不同的是,slf4j 使用编译期绑定的方式来确定绑定器,所谓编译期绑定就是所有的slf4j绑定器实现类都使用相同的全限定类名(StaticLoggerBinder),引入不同的slf4j绑定器jar包,但每一个的绑定器类名都是相同的,以此来实现动态替换的目的。
slf4j 在初始化阶段如果检测到类路径中同时存在多个绑定器会直接报错。
e.g.1
2
3
4
5
6SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/Users/chenxi20/.m2/repository/org/slf4j/slf4j-log4j12/1.7.25/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.25.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/Users/chenxi20/.m2/repository/ch/qos/logback/logback-classic/1.2.3/logback-classic-1.2.3.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.
SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory]
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: LoggerFactory is not a Logback LoggerContext but Logback is on the classpath. Either remove Logback or the competing implementation (class org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory loaded from file:/Users/chenxi20/.m2/repository/org/slf4j/slf4j-log4j12/1.7.25/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.25.jar). If you are using WebLogic you will need to add 'org.slf4j' to prefer-application-packages in WEB-INF/weblogic.xml: org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory
slf4j绑定包:
| groupId | artifactId | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| org.slf4j | slf4j-log4j12 | Log4j |
| org.apache.logging.log4j | log4j-slf4j-impl | Log4j2 |
| org.slf4j | slf4j-jcl | Commons Logging |
| org.slf4j | slf4j-jdk14 | JDK 自带的日志框架 |
| ch.qos.logback | logback-classic | Logback自带slf4j绑定包 |
e.g. 以 slf4j + log4j2 的组合为例,maven依赖配置如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23<!-- log4j2核心包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.9.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.9.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 绑定器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf4j核心包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
slf4j 桥接器:应用代码中使用别的日志接口,转成slf4j的方法
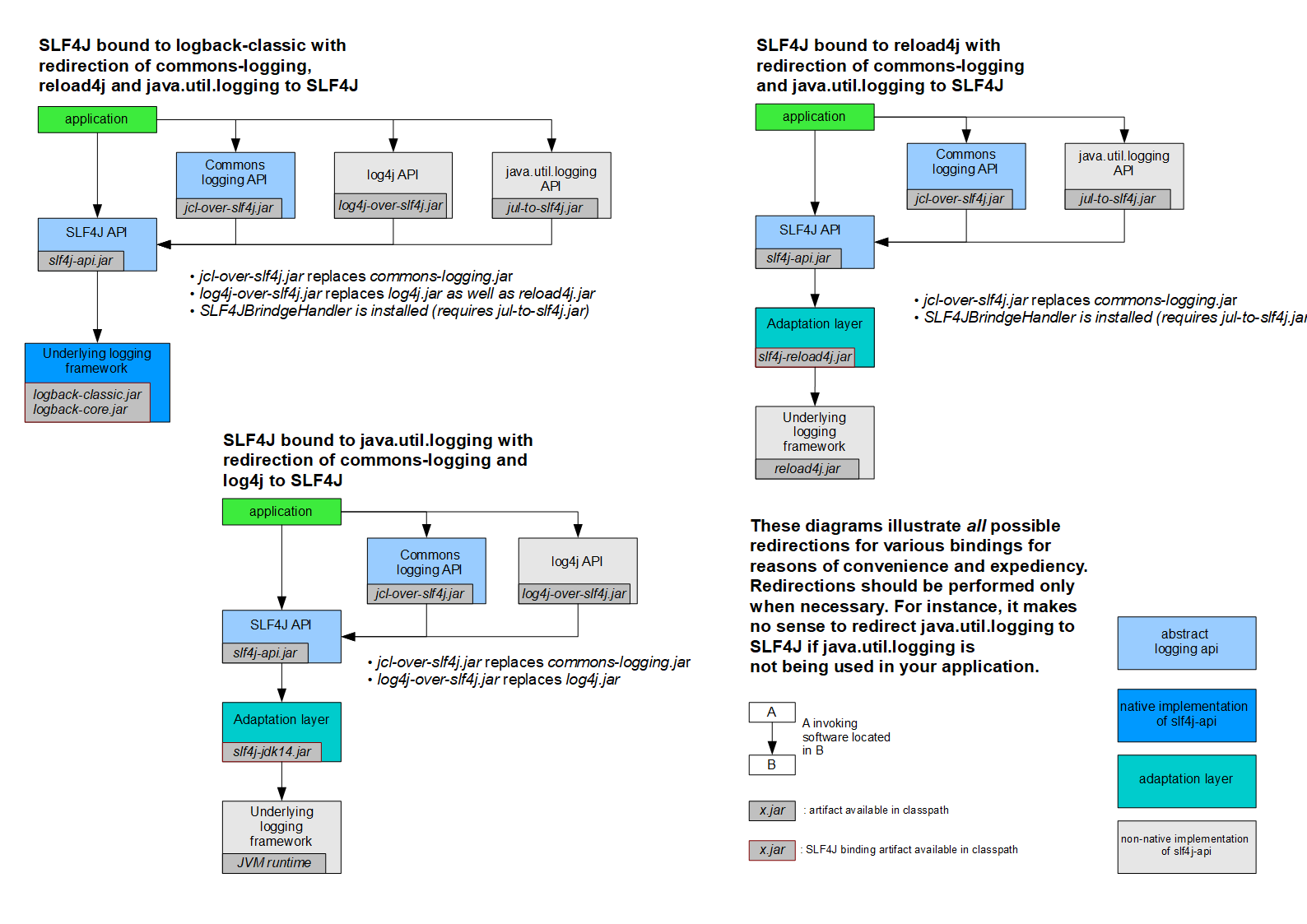
slf4j 桥接包:
| groupId | artifactId | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| org.slf4j | log4j-over-slf4j | Log4j |
| org.apache.logging.log4j | log4j-to-slf4j | Log4j2 |
| org.slf4j | jcl-over-slf4j | Commons Logging |
| org.slf4j | jul-to-slf4j | JDK 自带的日志框架 |
P.S.
log4j-over-slf4j vs log4j-to-slf4j :
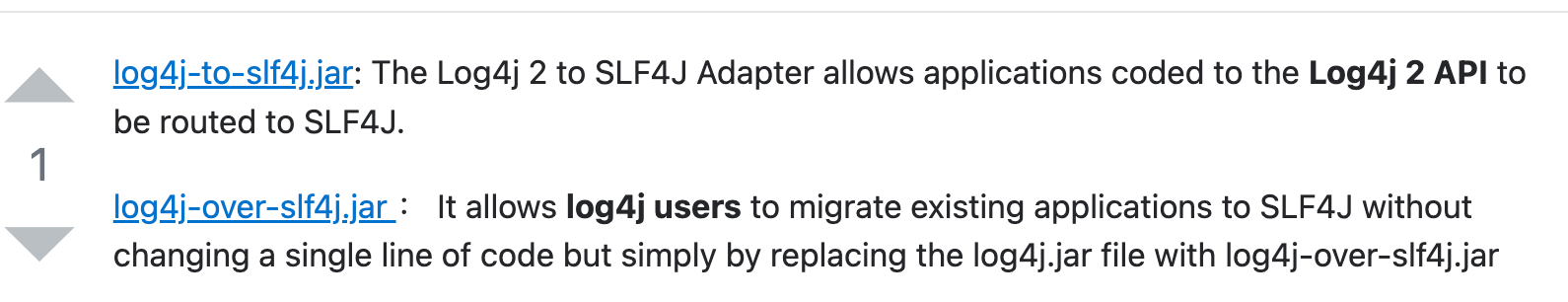
详见:difference-between-log4j-to-slf4j-and-log4j-over-slf4j
最佳实践
spring-boot 应用
spring-boot-starter-logging
spring-jcl 类似 jcl-over-slf4j 桥接器,接管应用代码对 jcl 的调用,不同之处在于会通过自动检测类路径jar包的方式选择使用 log4j2,还是 slf4j,如果前两者都不存在,兜底使用 jul。
注意,spring-boot-starter-logging 只引入了 jul-to-slf4j 和 log4j-to-slf4j (log4j2 桥接器) 两种依赖,没有提供 log4j-over-slf4j (log4j1 桥接器),加上其自带的 spring-jcl,这个 starter 对 jcl、jul、log4j2 三种日志框架都自动做了“桥接”处理,再加上默认引入的 logback 依赖,使得用户可以面对 slf4j API 编程,且默认日志框架实现为 logback。
因为该 starter 并没有对 log4j1 对桥接处理,如果应用里存在 log4j1 的使用,比如 curator, 就需要我们手动引入 slf4j 桥接包 log4j-over-slf4j,并且排除 log4j 依赖。
如果需要使用其他日志实现,如 log4j2,就需要将上述starter替换为:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-log4j2</artifactId>
</dependency>
Dubbo
类似 spring-jcl 这种带自动检测功能的日志门面还有 org.apache.dubbo.common.logger.LoggerFactory
拓展讨论
log4j vs log4j2
log4j:log4jlog4j 1 仅有一个 jar 包
log4j-api+log4j-core而 log4j 2 需要引入两个 jar 包。设计上分离了接口和实现
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!